In my last post, I went through some of the basics of whole blood transfusion. However, the focus was more on compatibility than function. Today, I’ll review an abstract that explored functionality of that blood transfused.
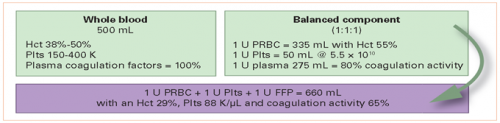
In theory, whole blood contains the usual array of clotting factors. It has been shown that high factor levels persist in whole blood, even when stored at room temperature. So in theory, additional clotting factor infusion should not be necessary.
The group at the University of Arizona explored adding 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4-PCC) to whole blood transfusion. The scanned three years of data in the TQIP database. They identified two groups of patients, those who received whole blood alone and those who received 4-PCC in addition to it. They were interested in the impact on total product transfused and the usual crude outcomes of hospital / ICU length of stay and mortality.
Here are the factoids:
- Only 252 patients in this entire database (tens of thousands of records in three years) received whole blood, and 84 of them also received 4-PCC
- The patients tended to be young (average age 47), 63% male, with moderate (median ISS 27), and blunt injury in 85%
- Administration of 4-PCC was associated with a significantly decreased transfusion requirement of both blood (5 vs 8 units) and plasma (3 vs 6 units), but not platelets
- ICU LOS was significantly lower in the 4-PCC group (5 vs 8 days), but there was no difference in hospital stay or in-hospital mortality
The authors concluded that 4-PCC given with whole blood was associated with a decrease in transfusion requirements and ICU length of stay, and that further studies were needed.
My comments: Well, this is certainly interesting and unexpected. Why would a clinician even think of giving 4-PCC when giving whole blood? It looks like a very rare occurrence in the dataset. Unfortunately, we can never find out. We can’t just go back and look in the charts. Perhaps these centers were using TEG or ROTEM during the resuscitation?
As always in these big databank analyses, the researchers can only control for the variables they can think of that are already present in the database. Although they were able to match the patient groups for the usual demographics, vital signs, injury patterns, comorbidities, and trauma center level, it is entirely possible that there were other factors in play.
Here are some questions for the authors and presenter:
- Why did you choose to do this study? Was there some clinical question that arose that triggered it? Something you found in the literature that suggested it?
- How do you explain the results, given that the factors in 4-PCC have been shown to persist at functional levels in whole blood? Why do you think less blood and plasma were needed?
- What needs to happen next? I agree that more research is needed to see if this association is real. How would you go about doing it?
Thanks for a very intriguing paper! Details will follow, I’m sure.
Reference: Four factor prothrombin complex concentrate in adjunct to whole blood in trauma-related hemorrhage: does whole blood replace the need of factors? EAST 2021, Paper 18.