Best Of: What Percent Pneumothorax Is It?
Frequently, radiologists and trauma professionals are coerced into describing the size of a pneumothorax seen on chest xray in percentage terms. They may something like “the patient has a 30% pneumothorax.”
The truth is that one cannot estimate a 3D volume based on a 2D study like a conventional chest xray. Everyone has seen the patient who has no or a minimal pneumothorax on a supine chest xray, only to discover one of significant size with CT scan.
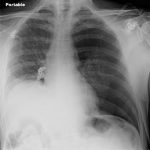
Very few centers have the software that can determine the percentage of chest volume taken up with air. There are only two percentages that can be determined by viewing a regular chest xray: 0% and 100%. Obviously, 0% means no visible pneumothorax, and 100% means complete collapse. Even 100% doesn’t really look like 100% because the completely collapsed lung takes up some space. See the xray at the top for a 100% pneumothorax.
If you line up 10 trauma professionals and show them a chest xray with a pneumothorax, you will get 10 different estimates of their size. And there aren’t any guidelines as to what size demands chest tube insertion and what size can be watched.
The solution is to be as quantitative as possible. Describe the pneumothorax in terms of the maximum distance the edge of the lung is from the inside of the chest wall, and which intercostal space the pneumothorax extends to. So instead of saying “the patient has a 25% pneumo,” say “the pneumothorax is 1 cm wide and extends from the apex to the fifth intercostal space on an upright film.”