The treatment of a “sucking chest wound” in the field has typically been with application of some type of occlusive dressing. Many times, a generic adhesive dressing is applied, typically the same kind used to cover IV sites. This is quick, easy, cheap, and readily available in the ambulance. But there is a danger that this could result in development of tension pneumothorax, because the dressing not only keeps air from getting in but also keeps any buildup of pneumothorax from getting out.
To avoid this, a number of vented products have been developed and approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These devices have some sort of system to allow drainage of accumulating air or blood, typically a one-way valve or drainage channels. They also need to stick well to a chest wall, which may have blood or other fluids that might disrupt the seal completely.
The US Army has a strong interest in making sure the products they use for this purpose work exactly as promised. The US Army Institute of Surgical Research examined 5 currently FDA-approved products to determine their ability to adhere to bleeding chest wounds, and to drain accumulating air and/or blood from the pleural space. They developed an open chest wound with active bleeding in a swine model.
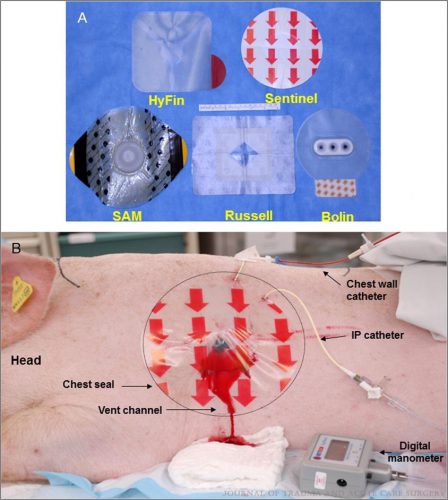
An open hemopneumothorax was created by infusing air and blood, the animal was stabilized, then additional aliquots of air and blood were infused to simulate ongoing bleeding and air buildup. The image below shows the 5 products used and the animal setup:
Here are the factoids:
- Creation of the open hemopneumothorax caused the intrapleural pressure to move toward atmospheric pressure as expected, resulting in labored breathing and reduced O2 saturation
- Sealing the wound with any of the chest seal products corrected all of the problems just noted
- Chest seals with one way valves did not evacuate blood efficiently (Bolin and SAM). The dressings either detached due to pooled blood, or the vent system clogged from blood clot.
- Seals with laminar channels for drainage (see the pig picture above) allowed easy escape of blood and air
- Success rates were 100% for Sentinel and Russell, 67% for HyFin, 25% for SAM, and 0% for Bolin
Bottom line: Prehospital providers need to be familiar with the products they use to cover open chest wounds. Totally occlusive dressings can result in development of a tension pneumothorax if there is an ongoing air leak from the lung. Vented chest seals are preferable for these injuries. Just be aware that vented seals with drainage channels perform much better than those that rely on a one-way valve.
Reference: Do vented chest seals differ in efficacy? An experimental
evaluation using a swine hemopneumothorax model. J Trauma 83(1):182-189, 2017.