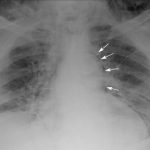
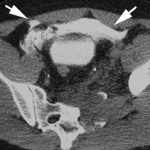
Recently, a Chinese man was in the news after having a four inch knife blade removed from his head after four years. What is the best way to deal with a problem like this?
First, get in the habit of imaging any body part with a penetrating injury. Retained objects can be as simple as gravel or as complicated as the knife blade above. And remember, some patients who have been stabbed present with a simple laceration but don’t want to tell you how they got it. Image before you close it!
Next, don’t remove it. This is common knowledge, but innocent looking objects (pencils, nails) can penetrate arteries and keep them from bleeding while embedded. Unpleasant and sometimes fatal bleeding can ensue if pulled out.
If you do not have specialists versed in the body regions involved in the injury, transfer immediately with the object secured in place. For objects penetrating minimally complex areas like the extremities, surgeons may opt to carefully remove it in the emergency department, or may elect to do so in the operating room.
Injuries to complex areas should undergo high resolution CT scanning so that 3D reconstruction can be performed if needed. The surgical specialists can then plan the operative approach. This is dictated by the anatomy of the area(s) involved and the architecture of the object (think about hooks and barbs). For objects located near critical areas, an operative exposure must be selected that provides access to all portions of it, and allows for rapid vascular control if needed.
This patient had a knife blade break off after he had been stabbed under the chin. It remained partly within the nasopharynx and the tip came to rest behind his left eye. His symptoms included headaches, stuffy nose and bad breath. The picture below shows the badly corroded blade in front of some of his radiographic images.