A number of surgical disciplines use antibiotic beads to deliver antimicrobial drugs to sites that may not have ideal serum penetration. Unfortunately, beads require multiple operations for placement and replacement until the desired effect is achieved.
What if there was a way of delivering antimicrobial therapy directly to the tissues that works for up to two weeks, then dissolves with no trace? A system that does this is being developed by engineers at Tufts University and the University of Illinois at Urbana. They created a small magnesium coil that can be heated using magnetic induction. It is enclosed in a silk pocket and then implanted into the infected tissues.
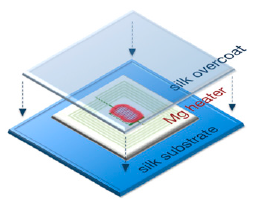
The tissues surrounding the device can be heated to different temperatures by placing an induction coil over it and delivering a specific amount of power.
It is also possible to deliver antibiotic doses directly to the tissue by embedding the drug into the silk pocket. As the coil heats up, the antibiotic is released from the fabric.
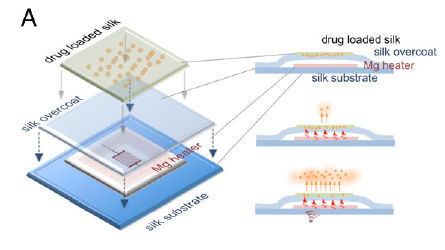
The magnesium coil normally dissolves within a few hours when immersed in water, and it takes a bit longer when in direct contact with living tissue. The silk pocket prolongs the time to dissolution, depending on how thick it is. In the rat experiment described in the paper, there was little or no trace after 15 days.
Bottom line: This exciting technology has the potential to simplify the delivery of antimicrobial therapy directly to deeper tissues for extended periods, without the need for a second procedure to retrieve the device. We’ll see how this implant works in studies in larger animals. I’m sure other derivative applications are soon to follow.
Reference: Silk-based resorbable electronic devices for remotely controlled therapy and in vivo infection abatement. Proceedings in the National Academy of Sciences. Published online November 24, 2014.

