Okay, time for the answer. This 12 year old crashed his moped, taking handlebar to the mid-epigastrium. Over the next 3 days, he felt progressively worse and finally couldn’t keep food down.
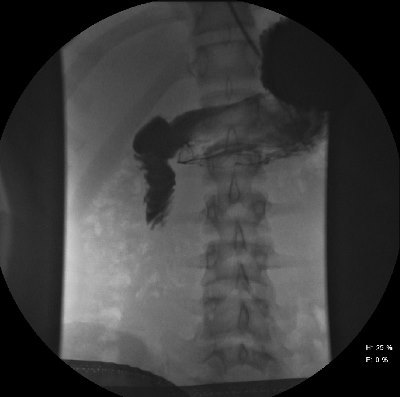
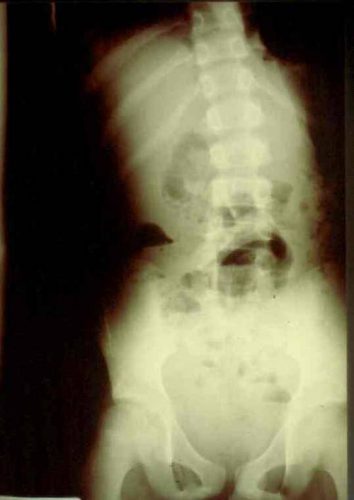
Mom brought him to the ED. The child appeared ill, and had a WBC count of 18,000. The abdomen was firm, with involuntary guarding throughout and a hint of peritonitis. The diagnosis was made on the single abdominal xray shown yesterday. Here is a close-up of the good stuff?
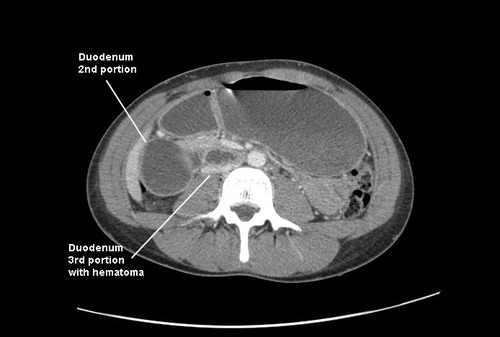
Emergency docs, your differential diagnosis list with this history is a pancreatic vs a duodenal injury based on the mechanism.
Classic findings for duodenal injury:
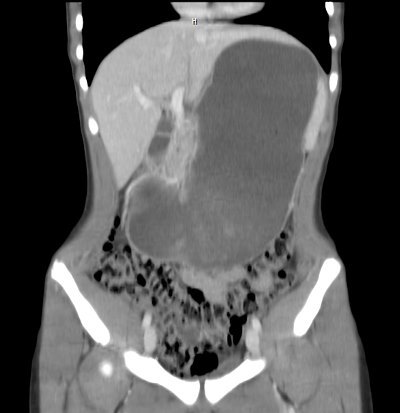
- Scoliosis with the concavity to the right. This is caused by psoas muscle irritation and spasm from retroperitoneal soiling by the duodenal leak.
- Loss of the psoas shadow on the right. Hard to see on this xray, but the left psoas shadow is visible, the right is not. This is due to fluid and inflammation along this plane.
- Air in the retroperitoneum. In this closeup, you can actually see tiny bubbles of leaked air outlining the right kidney. There are also bubbles along the duodenum and a few along the right psoas.
We fluid resuscitated first (important! dehydration is common and can lead to hemodynamic issues upon induction of anesthesia) and performed a laparotomy. There was a blowout in the classic position, at the junction of 1st and 2nd portions of the duodenum. The hole was repaired in layers and a pyloric exclusion was performed, with 2 closed drains placed in the area of the leak.
The child did well, and went home after 5 days with the drains out. Feel free to common or leave questions!