The standard of care in vascular access in trauma patients is the intravenous route. Unfortunately, not all patients have veins that can be quickly accessed by prehospital providers. Introduction of the intraosseous device (IO) has made vascular access in the field much more achievable. And it appears that most fluids and medications can be administered via this route. But what about iodinated contrast agents via IO for CT scanning?
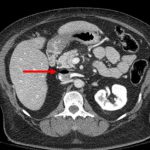
Physicians at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit have just published a case report on the use of this route for contrast administration. They treated a pedestrian struck by a car with a lack of IV access sites by IO insertion in the proximal humerus, which took about 30 seconds. They then intubated using rapid sequence induction, with drugs injected through the IO device. They performed full CT scanning using contrast injected through the site using a power injector. Images were excellent, and ultimately the patient received an internal jugular catheter using ultrasound. The IO line was then discontinued.
This paper suggests that the IO line can be used as access for injection of CT contrast if no IV sites are available. Although it is a single human case, a fair amount of studies have been done on animals (goats?). The animal studies show that power injection works adequately with excellent flow rates.
The authors prefer using an IO placement site in the proximal humerus. This does seem to cause a bit more pain, and takes a little practice. A small xylocaine flush can be administered to reduce injection discomfort in awake patients. Additionally, the arm cannot be raised over the head for the torso portion of the scan.
Bottom line: CT contrast can be injected into an intraosseous line (IO) with excellent imaging results. Insert the IO in a site that you are comfortable with. I do not recommend power injection at this time. Although the marrow cavity can support it, the connecting tubing may not. Have your radiologist hand-inject and time the scan accordingly.
Note: long term effects of iodinated contrast in the bone marrow are not known. For this reason, and because of smaller marrow cavities, this technique is not suitable for pediatric patients.
Related post: Air embolism from an intraosseous line
Reference: Intraosseous injection of iodinated computed tomography contrast agent in an adult blunt trauma patient. Annals Emerg Med 57(4):382-386, 2011.