One of the most common injuries encountered by trauma professionals is blunt head trauma, and it’s one of the leading causes of death in young people. Keeping the level of intracranial pressure (ICP) within a specified range is one of the basic tenets of critical neurotrauma care in these patients. Most trauma centers have sophisticated algorithms that provide treatment guidance for various levels of ICP or cerebral perfusion.
The vast majority of patients with severe head injuries are transported to the hospital in some type of ambulance. Obviously, the exact ICP level is not known during transport because no monitoring device is present. We can sometimes infer that ICP is elevated if the patient has a Cushing response (wide pulse pressure and bradycardia) or unequal pupils. But for the most part, we assume that ICP is in a steady state during the ambulance ride.
But here’s something I never considered before: can ambulance acceleration or deceleration change the ICP through shifting of the brain or cerebrospinal fluid?
Patients are generally loaded into ambulances head-first, with their feet toward the back door. Frequently, they must be positioned supine in consideration of possible thoracic or lumbar spine injury. This position itself may lead to an increase in ICP. But what happens when the ambulance is hitting the brakes as it approaches a light or stop sign? As the patient’s weight shifts toward the top of the head, so does the CSF, spinal cord, and brain. Couldn’t this, too, increase ICP?
The anesthesiology group at the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, Holland performed a very novel study to assess this very thing. They recruited twenty participants in whom they evaluated ICP in various positions during acceleration and deceleration.
No, the subjects did not have an actual invasive ICP monitor inserted.
The authors used a novel way to infer pressures: optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD). The optic nerves are direct extensions of the brain, and CSF travels freely in the nerve sheath. As ICP rises, the diameter of the nerve sheath increases. The subjects were fitted with a special helmet with two devices mounted on it. The first was a 7.5 Mhz ultra-sound probe focused on the back of the eye. The second was an arm with an orange dot on the end. This was adjusted so that the ultrasound probe was pointing at the optic nerve sheath when the other eye was focused on the dot. Subjects just watched the dot and measurements streamed in! Crude but very effective.
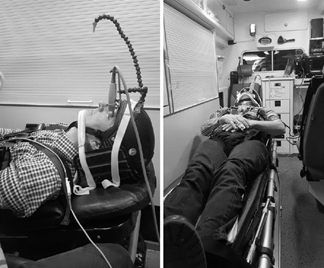
Baseline measurements were taken without acceleration or deceleration, then repeated when accelerating to 50 km/hr and decelerating to a stop.
Here are the factoids:
- A total of 20 subjects were tested, and their oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and pulse were identical pre- and post-test
- Baseline ONSD was about 5mm; a relevant change in diameter was determined to be more than 0.2 mm
- Lying supine, the ONSD in nearly all subjects increased from an average 4.8 to 6.0 mm during deceleration
- With the head raised to 30º, most values remained steady (from 4.8 to 4.9 mm) during deceleration
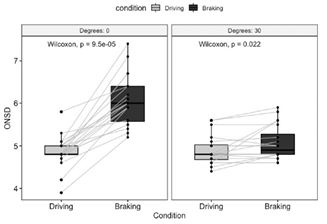
The left block shows the increase in size of the optic disk with braking while supine. The right one demonstrates that this effect is neutralized by elevating the head 30º.
Bottom line: This is a small, simple, and creative study, yet the results are very interesting! It is clear that optic nerve sheath diameter increases significantly during deceleration in patients who are supine. And this effect is eliminated if the head of bed is elevated 30º.
Unfortunately, we have no idea how the change in ONSD corresponds to absolute values of, or relative increases in, ICP. Does a change of 1.2mm indicate a 5 torr increase in ICP? A 5% increase? Is it proportional to the absolute ICP? We just don’t know.
But the data is clear that a measurable change does occur. Until better data is available, it may be desirable to transport patients with serious head injuries with the head elevated to 30º if there are no concerns for lower spine injury. Or failing that, make sure the driver does not have a lead foot!
Reference: Ambulance deceleration causes increased intra cranial pressure in supine position: a prospective observational prove of principle study. Scand J Trauma Open Access 29:87, 2021.