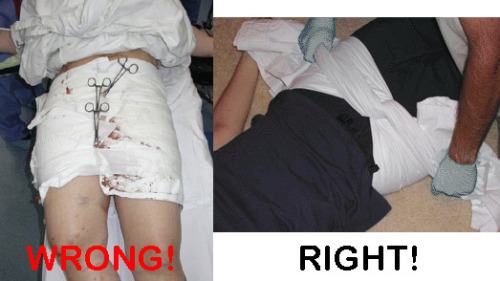
Yesterday, I detailed some pelvic binders commonly available in the US. Today, I’ll go through the (little) science there is regarding which are better than others.
And remember, tomorrow I’ll show you how to make a free pelvic binder out of stuff that all medics have in their rig.
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing one of these products. They are:
- Does it work?
- Does it hurt or cause skin damage?
- Is it easy to use?
- How much does it cost?
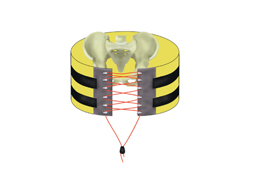
It’s difficult to determine how well binders work in the live, clinical setting. But biomechanical studies can serve as a surrogate to try to answer this question. One such cadaver study was carried out in the Netherlands a few years ago. They created one of three different fracture types in pelvis specimens. Special locator wires were placed initially so they could measure bone movement before and after binder placement. All three of the previously discussed commercial binders were used.
Here are the factoids:
- In fracture patterns that were partially stable or unstable, all binders successfully closed the pelvic ring.
- None of the binders caused adverse displacements of fracture fragments.
- Pulling force to achieve complete reduction was lowest with the T-POD (40 Newtons) and highest with the SAM pelvic sling (120 Newtons). The SAM sling limits compression to 150 Newtons, which was more than adequate to close the pelvis.
So what about harm? A healthy volunteer study was used to test each binder for tissue pressure levels. The 80 volunteers were outfitted with a pressure sensing mat around their pelvis, and readings were taken with each binder in place.
Here are the additional factoids:
- The tissue damage threshold was assumed to be 9.3 kPa sustained for more than 2-3 hours based on the 1994 paper cited below.
- All binders exceeded the tissue damage threshold at the greater trochanters and sacrum while lying on a backboard. It was highest with the Pelvic Binder and lowest with the SAM sling.
- Pressures over the trochanters decreased significantly after transfer to a hospital bed, but the Pelvic Binder pressures remained at the tissue damage level.
- Pressures over the sacrum far exceeded the tissue damage pressure with all binders on a backboard and it remained at or above this level even after transfer to a bed. Once again, the Pelvic Binder pressures were higher. The other splints had similar pressures.
And finally, the price! Although your results may vary due to your buying power, the SAM sling is about $50-$70, the Pelvic Binder $140, and the T-POD $125.
Bottom line: The binder that performed the best (equivalent biomechanical testing, better tissue pressure profile) was the SAM sling. It also happens to be the least expensive, although it takes a little more elbow grease to apply. In my mind, that’s a winning combo. Plus, it’s narrow, which allows easy access to the abdomen and groins for procedures. But remember, whichever one you choose, get them off as soon as possible to avoid skin complications.
References:
- Comparison of three different pelvic circumferential compression devices: a biomechanical cadaver study. JBJS 93:230-240, 2011.
- Randomised clinical trial comparing pressure characteristics of pelvic circumferential compression devices in healthy volunteers. Injury 42:1020-1026, 2011.
- Pressure sores. BMJ 309(6959):853-857, 1994.