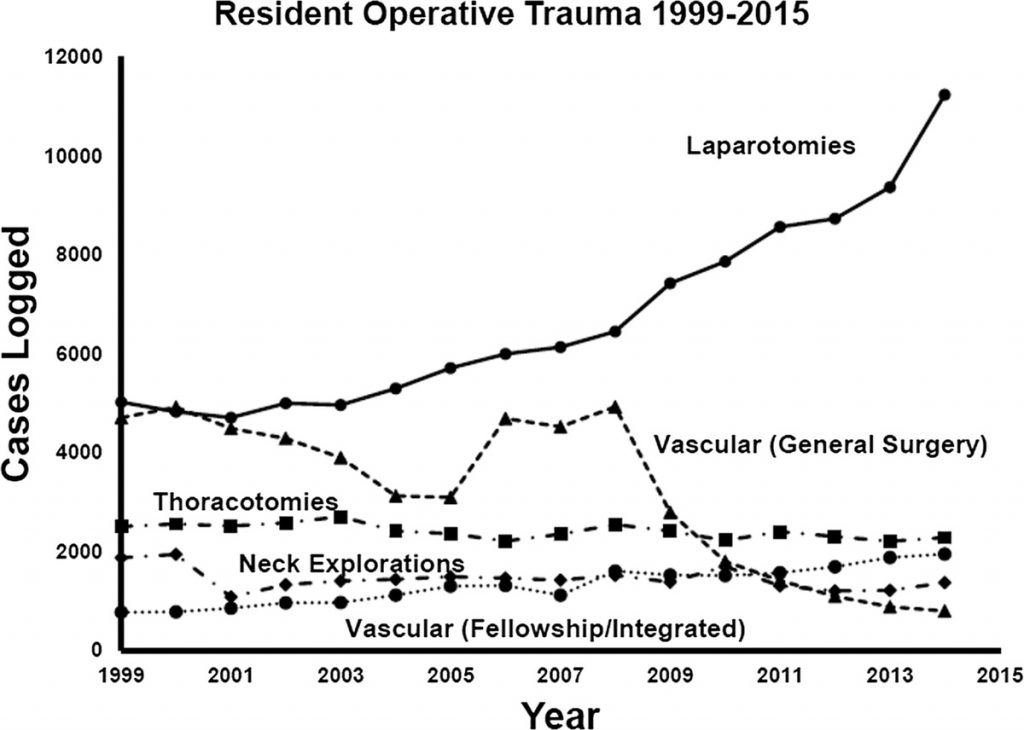
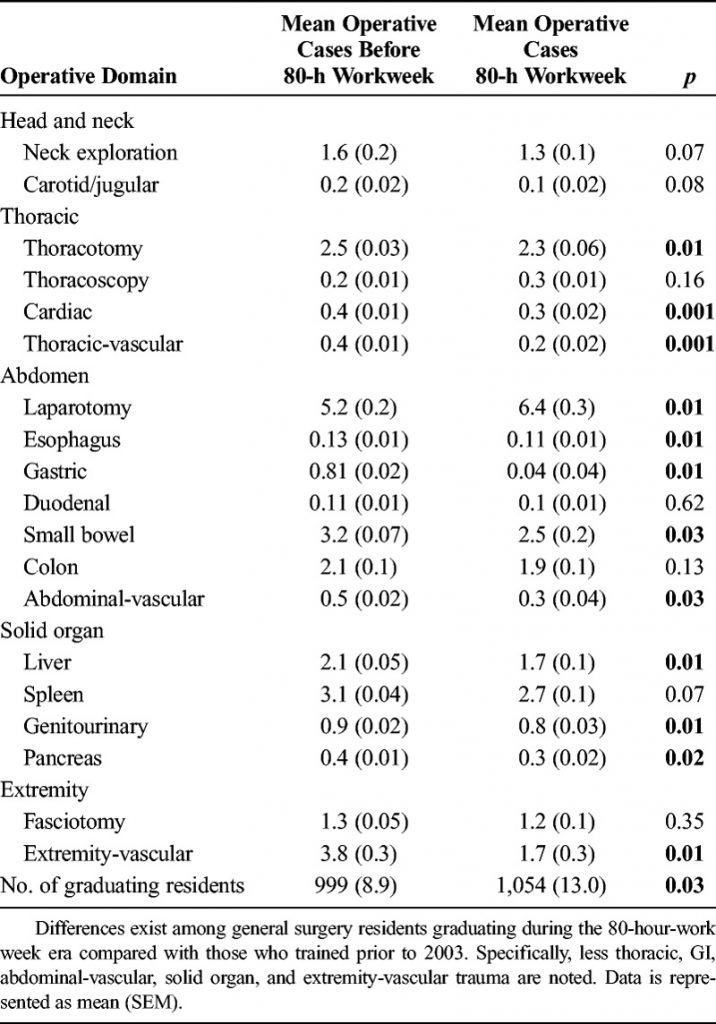
In my last post, I detailed an older study that did not show much of an impact from having the trauma surgeon in-house at all times. However, like many of the papers published on this over the years, it suffered from small numbers and questionable endpoints.
A group in the Netherlands sought to analyze everything they could find on the topic and perform a meta-analysis and systematic review. They scanned the literature beginning in 1976, the year that the ACS Committee on Trauma published the first resource criteria for trauma center verification. A total of 16 studies (RCTs and observational) that included information on over 64,000 patients were carefully selected for study. The endpoints of interest were in-hospital mortality and several process measures including lengths of stay and time to OR and CT.
Here are the factoids:
- In-house mortality significantly decreased with in-house surgeons, with a relative risk reduction of 14% (from good quality papers, primarily published after 2000)
- ICU length of stay was shorter with an in-house surgeon in four studies, longer in one
- Hospital length of stay was shorter with the in-house surgeon in four studies, longer in two
- Time to OR was significantly faster in seven studies with an in-house surgeon, but no difference was seen in five
- Time to CT was shorter in one study and no different in four with the in-house surgeon
Bottom line: What does it all mean? We have been led to believe that doing a meta-analysis / systematic review can help us make sense of a group of papers with flaws such as low numbers, questionable design, or bias. This work shows that this is not necessarily the case.
Think of a good meta-analysis as a set of eyeglasses focused on a selected body of literature. The blurry individual papers are grouped together and brought into better focus by the meta-analysis process. However, the final visual acuity is still determined by the overall quality of the individual research works.
If the overall quality is low, things will remain somewhat blurry even after meta-analysis. As individual paper quality improves, or the papers at least include some higher quality data mixed in with chaff, the overall clarity of the meta-analysis gets better and better.
In this meta-analysis, all papers included mortality information. There is enough there to show the association of an in-house trauma surgeon and lower mortality. But as with all association studies, it is impossible to say that the improved survival is due to the surgeon alone. There are many other factors that were not or could not be evaluated in the studies that might parallel the presence of the surgeon. And similarly with the process measures (LOS, time to resource use), we are generally seeing a preponderance of that show a positive effect. But it’s still not open and shut.
I interpret this meta-analysis / systematic review as overall positive and supportive of having an in-house surgeon. It definitely dovetails with my own experience with in-house call over the past 38 years. I recognize the crudeness of the outcome measures selected, and our inability to quantify more subtle benefits. And we still haven’t fully figured it out the value, even after over 20 years of decent studies. This means we probably won’t ever fully know the answer since the system we work in continues to shift, potentially rendering the older information obsolete.
We will most likely continue with in-house call at highest-level trauma centers for the foreseeable future. In my opinion, and as is suggested by most of the literature, that is a good thing for our patients.
Reference: In-house versus on-call trauma surgeon coverage: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery: August 2021 – Volume 91 – Issue 2 – p 435-444,